Describe insider risk management solutions to protect against internal threats
Microsoft 365 contains a set of policy tools to allow organizations to identify risky behaviors and activities as well as to act on those alerts. This feature is known asinsider risk management (IRM). IRM is located inside the Microsoft 365 compliance portal athttps://compliance.microsoft. com/insiderriskmgmt. IRM combines components from DLP, sensitivity labels, natural language processing (NLP), sentiment analysis, access-control signals, and triggering events to quickly alertorganizations to risks such as potential data theft by a departing employee or sensitive information leaks.
Microsoft 365 IRM is designed to help mitigate various internal risks, such as the following:
- Data theft by a terminated or departing employee
- Intentional or unintentional leaking of sensitive information
- Violations of internal corporate policy, such as offensive language, cyber-bullying, harassment, and threats
These risks (along with others) can be identified and investigated through the IRM process and workflow, as follows:
- Policies: IRM policies are used to define in-scope users and risk indicators.
- Alerts: Alerts are generated when risk indicators for in-scope users are triggered. These alerts allow administrators to determine the risk status and potentially begin triage actions.
- Triage: During triage, analysts review the alerts in detail and decide on the action to take, creating a case to track and work through the alert, adding the alert to an existing case, or dismissing the alert.
- Investigate: If analysts create cases or add alerts to existing cases, staff can continue to work on and investigate the data in those cases.
- Action: Once a case has been investigated, analysts can resolve the case, generate a notice to the employee, or escalate the case for further action and investigation.
Policies are configured via templates in five categories (two categories are generally available and three are in preview), as shown in Figure 10.12:
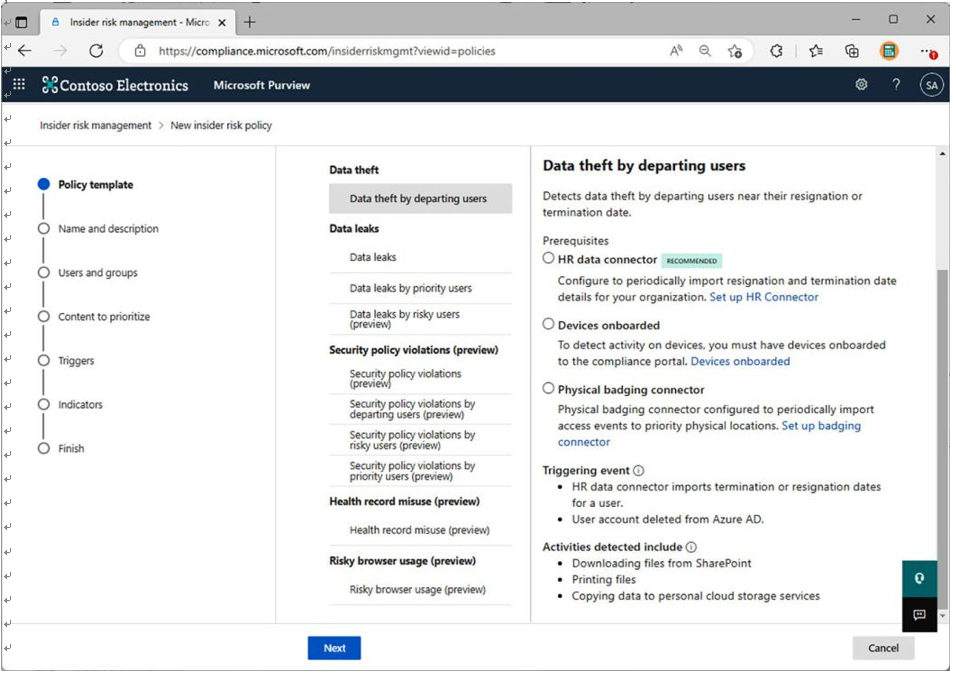
Figure 10.12 – Policy templates
A complete list of categories and templates is listed in Table 10.2:
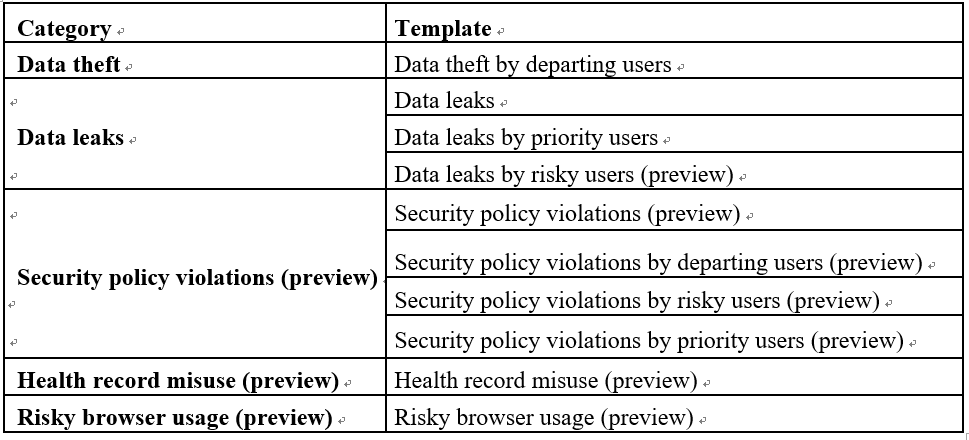
Table 10.2 – Policy template descriptions
Many IRM scenarios require configuring DLP policies as well as identifying groups of users to monitor. Some policy templates require devices onboarded with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, communication compliance policies, or integration with human resource information systems (HRISs) or security badging systems.
In addition to configuring the policy templates and DLP prerequisites, there are additional data connectors that can be used to import signaling information to help provide more context for risk indicators, as follows:
- Microsoft 365 Human Resources (HR) connector: The HR connector can be used to import data from risk management and HR information system platforms. The connector adds indicator data for employment status and dates, termination status, job-level change status, and other HR-related data fields.
- Physical badging connector: This connector supports importing data from physical access control systems, including data such as access point identifiers (IDs), time and date values,user IDs, and whether the attempt was successful. In order to correlate access control data with user identities, you’ll need to configure the Microsoft 365 HR connector as well. For more information on the Microsoft 365 HR connector, seehttps://learn.microsoft.com/ en-us/microsoft-365/compliance/import-hr-data.
• Microsoft Healthcare connector: IRM can be configured with healthcare connectors to import CSV data from electronic medical record systems. If you want to configure the Health record misuse policy, you’ll need to configure a healthcare connector.
IRM capabilities can contribute to compliance controls and improve not only your organization’s compliance adherence but overall security as well.
IRM Configuration Deep Dive
While deep IRM knowledge isn’t necessary for the MS-900 exam, you can expand your knowledge of the platform by visiting https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/ compliance/insider-risk-solution-overview.
IRM strategies may include configuring not only DLP policies but also things such as Exchange Online transport rules or Microsoft Teams Information Barriers to prevent groups of individuals from communicating with each other. All these components work together to mitigate the overall risk and exposure for an organization.
IRM requires one of the following subscriptions:
- Microsoft 365 E5 (or comparable) subscription
- Microsoft 365 E3 (or comparable) subscription with the E5 (or comparable) Compliance add-on
- Microsoft 365 E3 (or comparable) subscription with the E5 (or comparable) IRM add-on
Next, you’ll explore the concept of eDiscovery and how you can use it to fulfill litigation discovery requirements.

