Compliance scoring
As you learned in the previous section, Compliance Manager is a tool that you can use to track progress against various controls and standards. Your compliance score is a dashboard that helps you visualize your progress toward completing the recommended improvement actions within the applicable controls.
When you launch Compliance Manager, your score is prominently displayed. An example is shown in Figure 10.2:
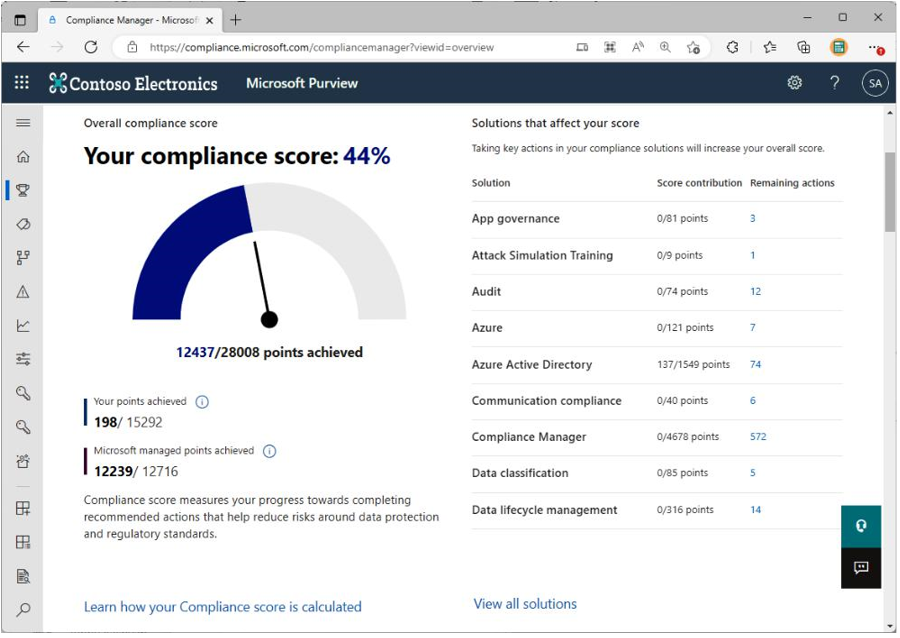
Figure 10.2 – Compliance Manager dashboard
At the bottom of the graph depicted in Figure 10.2, you’ll notice your score is represented as a fraction:
points achieved/points available.
Your score is made up of three primary parts, as follows:
- Improvement action score: Each action is assigned a different value, based on the impact that it has or the potential risk condition that it’s addressing. For example, configuring the message quarantine settings in Exchange Online protection is a lower improvement action score than enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Control score: The control score is the total of the points earned within a particular control, risk, or configuration item. This score is added to your compliance score when the actions have been implemented successfully and they pass the automated testing.
- Assessment score: This score is the total value of individual control scores.
The compliance scores are calculated using the improvement action scores. Each Microsoft action is counted once, as is each technical action that you manage. Each non-technical action (such as a policy or documentation) is counted once per group since these are generally viewed as organization-wide activities that only need to be completed one time.
Your tenant’s compliance score is initially calculated using the default Microsoft Data Protection Baseline assessment, which pulls controls and standards from NIST and CSF, ISO, FedRAMP, and GDPR.
Compliance Manager then automatically recalculates your score based on improvement actions that you perform. Generally, the results of improvement actions are visible in your compliance score the following day.
As mentioned earlier, actions can be technical and non-technical. Technical actions require configuration of the platform and are scored once per action, regardless of how many groups they belong to. Non-technical actions are managed outside the Microsoft 365 platform and recorded manually in Compliance Manager. Non-technical actions are classified as either documentation or operational and are scored at a group level.
So, now that you know how the overall score is calculated, you will learn how actions are assigned scores.
An action’s score is based on whether the action is mandatory or discretionary, as well as whether the action is preventative, detective, or corrective. This is described in more detail here:
- Mandatory: These are actions that can’t be bypassed by the user (either accidentally or intentionally). MFA and system password policies are examples of mandatory actions.
- Discretionary: These actions, however, rely on the user following a policy with no technical enforcement. For example, you may implement a policy that instructs each user to swipe a proximity badge to enter a building instead of holding the door open for a group of people.
- Preventative: If an action is designed to mitigate a specific risk, it is classified as a preventative action. Implementing an MFA solution is an example of a preventative action designed to minimize the impact of leaked credentials.
- Detective: These are monitoring actions designed to identify anomalous behavior. Deploying an application to detect port scanners or regular audits of electronic discovery (eDiscovery) logs are actions designed to find potentially malicious behaviors.
- Corrective: Corrective actions minimize or repair the damage incurred during an incident. Restoring a system from backups after a breach is an example of a corrective action.
Table 10.1 depicts the scores assigned to each category of actions:
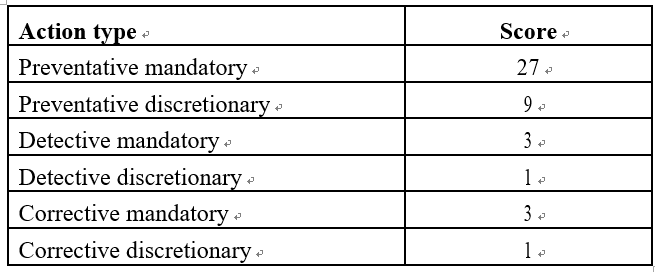
Table 10.1 – Action types and scores
You can review an individual action’s score by selecting Improvement actions in Compliance Manager, as shown in Figure 10.3:
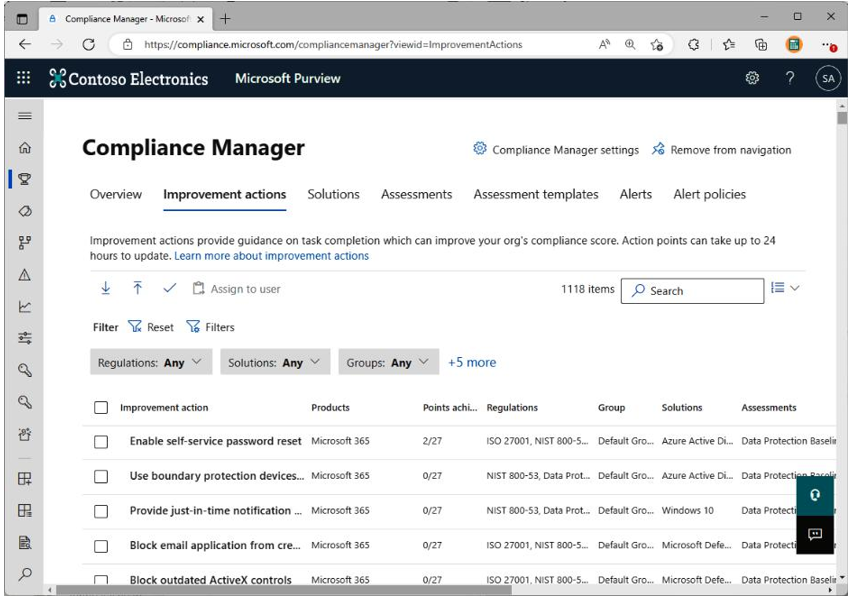
Figure 10.3 – Improvement actions
Next, you’ll learn about Microsoft 365 service configurations and auditing actions that support regulatory compliance.

